Adult Mental Health

 Introduction
Introduction
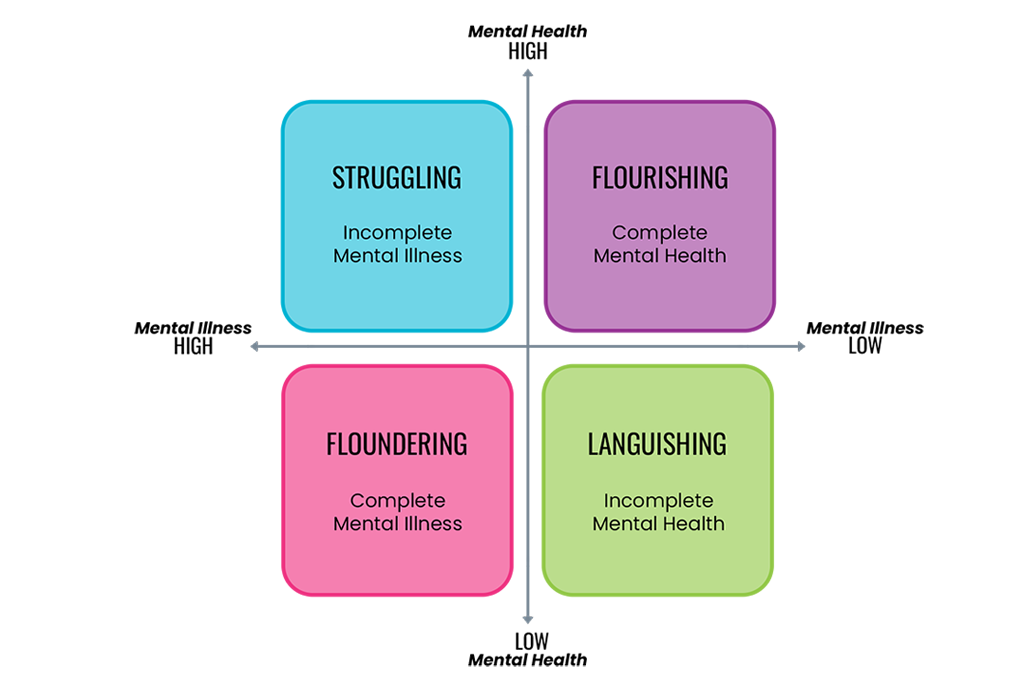
Everyone has mental health and wellbeing. People with mental illness can have good mental wellbeing which enables them to flourish, to be resilient and to manage their illness. Equally, those without mental illness can experience poor mental wellbeing which can have a detrimental impact on their functioning and day-to-day life causing them to languish. Good mental health is more than the absence of mental illness, it also requires the presence of something positive i.e. mental wellbeing. The mental health dual axis model (Keyes & Lopez, 2002) demonstrates this:
1 in 4 people have a mental health problem in any given year, and half of adult mental health problems start by the age of 14. The vast majority of people who have a diagnosed mental health condition is of a common mental health disorder such as stress, anxiety or depression.
These conditions can be considered one that people may experience for a limited period of time and can effectively recover from. A small proportion of people have long-term severe and enduring mental health conditions.
Mental health status strongly influences health, social and economic outcomes and as a result both mental ill-health and poor wellbeing can have a significant negative impact on the lives of people.
 Why is it important to Population Health?
Why is it important to Population Health?
A population health approach is important to help reduce health inequalities. Health inequalities are ultimately about differences in the status of people’s health, but the term is also commonly used to refer to differences in the care that people receive and the opportunities that they have to lead healthy lives, both of which can contribute to their health status.
Related to mental health:
- People with serious mental illness (SMI) die 15-20 years early
- People with mental illness are less likely to be employed
- Black and Asian males have much higher rates of psychotic disorder.
 The Derbyshire Population Health Approach
The Derbyshire Population Health Approach
The Derbyshire Population Health Approach focuses on prevention, population health, evidence-informed practices, causes, and collaboration. It emphasises proactive measures to prevent health issues, tailors interventions to specific populations, incorporates evidence-informed practices, addresses underlying causes, and promotes collaboration for effective action.
When considering the topic of Mental Health within The Derbyshire Population Health Approach:
• Prevention
A preventative approach is vital to reduce the number of people who may develop mental ill health, to support people to recover from mental ill health and to help people manage long term mental ill health.
Preventative measures include promoting positive mental wellbeing, reducing stigma associated with mental health conditions to change the culture, and early identification of mental health issues. These are delivered through awareness raising campaigns, training and upskilling people to play a proactive and supportive role.
A preventative approach includes all of the factors that influence mental health such as the wider determinants of health (e.g. housing, income, employment) risky behaviours (e.g. substance misuse, gambling) and key protective factors such as social connectivity.
Initiatives that support healthy lifestyles, help people to develop resilience and skills to cope and connect people to peer support play a key role in prevention.
• Population
Mental health is a universal aspect of human experience, impacting individuals across all walks of life. However, specific groups within the adult population of Derbyshire face a higher risk of experiencing mental ill health due to a variety of circumstances or life events. Recognising and understanding these disparities is foundational to delivering targeted and effective mental health services. Key groups identified through long-term evidence as being at higher risk include:
- Children and Young People: Early-life stressors and developmental challenges can significantly impact mental health, making early intervention critical.
- Parents, particularly new mothers, face unique pressures that can affect their mental wellbeing.
- Older Adults often experience factors such as isolation, bereavement, and physical health issues that can exacerbate mental health conditions.
- Individuals with Disabilities may encounter daily stresses and barriers that impact their mental health.
- Clinically Extremely Vulnerable Individuals face increased anxiety and mental health challenges, particularly highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- LGBTQ+ Individuals often deal with societal stigma, discrimination, and personal identity issues, influencing their mental health.
- People from Ethnic Minority Backgrounds can experience cultural, economic, and social stressors that affect mental health.
By leveraging data and insights, Derbyshire aims to tailor services and support to meet the nuanced needs of these groups, ensuring equitable access to mental health care and fostering a supportive community for all.
• Evidence
The landscape of mental health research and policy is rich and evolving, with both longstanding trends and emerging insights shaping our understanding and approach to care. In the UK, several national strategies and clinical guidelines inform evidence-based practices for mental health:
- The NHS Long Term Plan outlines ambitions to transform mental health care, emphasising early intervention, integrated support, and enhancing community-based care.
- NICE Guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for treating and managing mental health conditions across diverse populations and settings.
- Mental Health Act Review: Recent reviews of the Mental Health Act emphasise respecting patients’ rights and ensuring that care and treatment are as therapeutic as possible.
- Office for Health Improvement and Disparities offer insights and data on population health, including mental health, guiding local public health strategies.
Incorporating these resources with local intelligence allows Derbyshire to employ an informed approach to mental health care, ensuring that interventions are not only grounded in solid evidence but also resonate with the specific needs and circumstances of the local population.
• Causes
Factors influencing adult mental health conditions include environmental stressors, socio-economic factors, lifestyle choices and genetics.
There are proven links between factors such as deprivation, gambling, inadequate housing, traumatic experiences, long term conditions and social isolation. Addressing the causes of the causes is of paramount importance.
A comprehensive approach that addresses these determinants is necessary for effective prevention, management and support.
• Collaboration
Collaboration amongst the voluntary sector, experts by experience, healthcare providers, mental health specialists, social services and community organisations is essential for a holistic approach to mental health care. This collaboration helps to enable prevention of mental ill health and access to support and treatment for people with mental health conditions. Joined Up Care Derbyshire is firmly founded on insight and collaboration between a wide range of local partners, including the voice of lived experience and coproduction.
 Latest Derbyshire Data
Latest Derbyshire Data
Trend Data
Derbyshire Quilt
Prevalence Maps of Derbyshire
The maps below illustrate various geographies for Derbyshire. LSOAs and MSOAs are geographical divisions used for statistical purposes, allowing for more detailed analysis of local data. In these maps, you can explore various health indicators and data for Derbyshire, providing valuable insights into the area’s health and wellbeing.